Choosing the right turntable
Everything you need to know.
Vinyl is back in fashion... Or rather, vinyl is always in fashion! In reality, it never truly disappeared, but its resurgence in recent years has led it to surpass CDs in sales in the music market.
Many new releases nowadays are available only as digital downloads or on vinyl. Of course, having vinyl records requires a turntable, which is not as simple as buying a CD player. There are many factors to consider when making such a purchase.

Choosing the right turntable depends on various factors such as budget, usage, personal preferences, and your level of experience with analog sound. Here is a guide to help you make the best choice based on your needs.
Defining the purpose of use
Home listening: If you want a turntable for personal listening and enjoying music at home, you should focus on sound quality and ease of use.
DJing: If you plan to use the turntable for DJing, you will need a durable model with specific features such as high torque and the ability to perform back-cueing.
Vinyl digitization: If you want to convert your vinyl collection into digital format, a turntable with a built-in USB output would be ideal.
Types of turntables
There are various types of turntables that differ in mechanism, control, and features. The main categories are as follows:
Belt-drive turntables
In belt-drive turntables, the rotation of the platter is achieved through a rubber belt that connects the motor to the platter.

- Better vibration isolation: The belt acts as a damper, reducing vibrations coming from the motor and thus improving sound quality.
- Higher sound quality: Many vinyl enthusiasts prefer belt-driven turntables because they produce a "musical" and more "natural" sound.
- Lower cost: Belt-driven turntables are typically more affordable, making them ideal for beginners.
However, there are also some drawbacks:
- Speed stability loss: The belt can loosen or wear out over time, affecting speed accuracy.
- Maintenance required: The belt may need replacement after years of use.
Direct-drive turntables
In direct-drive turntables, the platter is directly connected to the motor, without the use of a belt.

This design offers the following advantages:
Immediate response and speed stability: These turntables provide very stable speed and an instant start of rotation, which is ideal for DJs who need immediate control over the record.
Durability: Direct-drive turntables are generally more durable and require less maintenance since there is no belt that could wear out.
DJ features: Many direct-drive models offer functions such as back-cueing, which are essential for DJing.
However, these turntables also have some disadvantages:
Potential vibrations: Since the platter is directly connected to the motor, vibrations can transfer to the record, slightly affecting sound quality.
Higher cost: Direct-drive turntables are usually more expensive, which might discourage beginners.
The choice between a belt-drive turntable and a direct-drive turntable is one of the key dilemmas faced by vinyl enthusiasts. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the selection largely depends on the user's needs and preferences. At the end of the day, it's a matter of personal preference.
Idler-Drive turntables
Idler-drive turntables are a less common but historically significant type of turntable that uses a rubber idler wheel to transfer motion from the motor to the platter. This wheel is positioned between the motor spindle and the platter, directly driving the platter's rotation. This design was popular in the mid-20th century, particularly in the 1950s and 1960s, before belt-drive and direct-drive systems became dominant.

Advantages:
High torque: Idler-drive turntables typically offer high torque, meaning the platter can reach full speed quickly and maintain stable rotation, making them ideal for radio broadcasts and DJ use in their time.
Durability: The idler wheel system is generally durable and robust, capable of supporting heavy platters, which enhances speed stability.
Disadvantages:
Noise and vibrations: The direct contact between the idler wheel and the platter can cause more noise and vibrations, potentially affecting sound quality.
Maintenance: The rubber idler wheel can harden or wear out over time, leading to slippage or other issues. Replacing the wheel can be challenging due to the rarity of spare parts.
Less common: As a vintage technology, idler-drive turntables are less common today, and finding spare parts or repairs can be more difficult.
Although idler-drive turntables have largely been replaced by belt-drive and direct-drive systems, they are still appreciated by some audiophiles and collectors for their unique sound characteristics and historical significance.
Automatic turntables
These turntables can start and stop playback automatically at the press of a button. The tonearm automatically moves over the record and back when the record finishes.
Semi-automatic turntables
In these, playback starts manually, but the tonearm automatically returns to its resting position at the end of the record.
- Function: The tonearm is placed on and/or returns automatically at the end of the record.
- Advantages: More convenience and protection for the record and needle.
- Suitable for: Beginners and those who prefer ease of use.
Manual turntables
The user manually moves the tonearm over the record to start playback and must do the same in reverse at the end. These turntables offer more control to the user.
- Function: The user must manually place and remove the tonearm.
- Advantages: Typically provide better sound quality and have fewer mechanical parts that can malfunction.
- Suitable for: Audiophiles who want more control and better sound quality.
USB turntables
These turntables have a USB port, allowing the digitization of vinyl records into MP3 or other audio formats. They are useful for those who want to store their music digitally.
Build quality and materials
The build quality and materials used in turntables play a crucial role in their performance and long-term durability. A high-quality turntable not only ensures better sound performance but also offers a longer lifespan, reduced maintenance needs, and an overall improved user experience.
Platter materials: The platter is one of the most important components of a turntable as it directly affects speed stability and vibration reduction. High-quality platters are typically made from materials like aluminum, acrylic, or glass. These materials are heavy and durable, providing better vibration absorption and reducing sound distortion.
Chassis materials: The chassis or base of the turntable must be sturdy and durable to minimize vibrations and noise that can affect sound quality. The best turntables use materials like MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard), aluminum, or even solid wood for the chassis construction. These materials provide greater stability and prevent environmental vibrations from affecting the record playback.
Tonearm: The tonearm should be both lightweight and rigid to ensure accurate tracking of the record. It is usually made from materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, or specialized metal alloys. These materials offer the necessary combination of lightness and rigidity, reducing noise and improving the precision of sound reproduction.
Anti-vibration feet: The feet of a turntable are designed to isolate it from environmental vibrations and shocks. They are usually made from materials such as rubber, silicone, or special polymers that absorb vibrations and protect the playback system from external noise.
The build quality and materials of a turntable are essential for its sound performance and long-term durability. Choosing a turntable made from high-quality materials can provide a better listening experience, longer-lasting durability, and less need for maintenance. Therefore, investing in a well-constructed turntable can prove to be an excellent choice for vinyl enthusiasts.
Cartridge and stylus
Types of Cartridges:
Moving Magnet (MM):
In a Moving Magnet (MM) cartridge, the movements generated by the stylus (needle) as it reads the grooves of the record are transferred via the cantilever. With the cantilever's movements controlled by an internal suspension system, a magnet is positioned at the end of the cantilever. As the stylus moves, so does the magnet. The movement of the magnet interacts with fine coils of wire placed nearby inside the cartridge, creating a voltage. This generates an electric current that is then transferred through the tonearm to the rest of the system via connected wires. This current is amplified and ultimately produces the sound output heard through your speakers. MM cartridges are generally more affordable and easier to maintain.
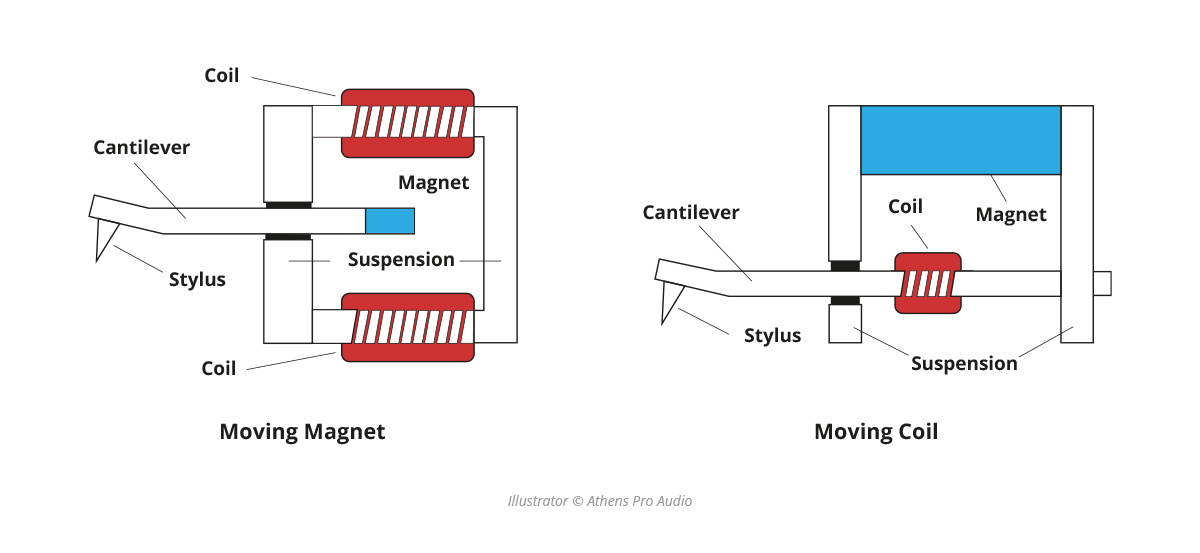
Moving Coil (MC):
Moving Coil (MC) cartridges work in a very similar way, but the roles of the magnet and coil are essentially reversed. In these types of cartridges, instead of the magnet moving as the stylus reads the grooves, the wire coils move instead. This is considered a more efficient and effective way of converting motion into an electrical signal since the coils are lighter than the magnet, allowing for smoother movement. The electric signal for MC cartridges is sent to the rest of the system in the same way as MM cartridges. Moving Coil cartridges are typically more expensive due to the more sensitive and precise manufacturing process. They usually offer higher sound quality but are costlier and require more careful setup.
Upgrades:
Many turntables allow for cartridge upgrades to improve sound quality.
The tonearm
The tonearm of a turntable is one of the key components of the system and plays a crucial role in the sound quality produced by a vinyl record. Let's take a look at some key features and functions of the tonearm:
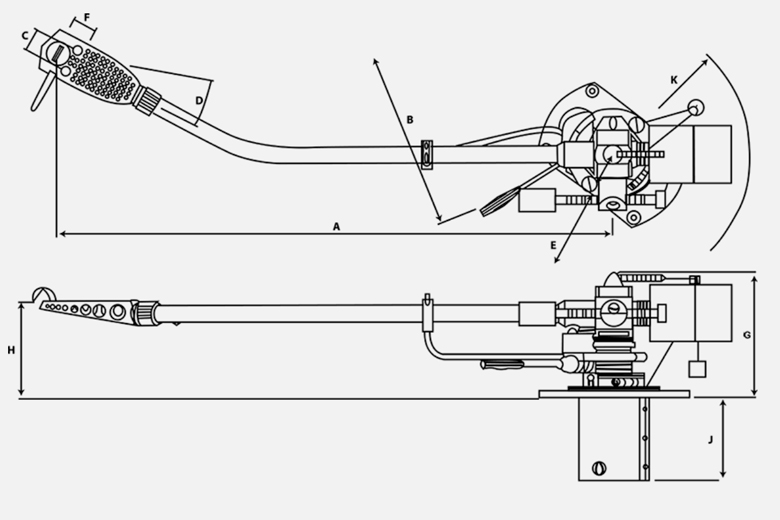
Function of the tonearm
The tonearm is responsible for positioning the stylus (needle) on the record and maintaining proper contact with the grooves of the vinyl. Its purpose is to ensure that the stylus follows the grooves' movements with maximum precision and minimal resistance or distortion.

Key Technical Features
Tonearm Length: The length of the tonearm affects the accuracy of the record’s playback. The most common types are short and long tonearms. A longer tonearm reduces angular distortion but requires more careful installation.
Material: Tonearms are made from various materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, or magnesium. The material plays an important role in stiffness and vibration damping.
Suspension and Counterweight System: The tonearm typically features a counterweight system that allows for the adjustment of the pressure applied by the stylus on the record. This setting is crucial to prevent damage to both the record and the stylus.
Pivot: The tonearm is mounted on a pivot that allows it to rotate freely, enabling it to follow the grooves of the record from start to finish.
Anti-skating: This mechanism prevents the stylus from sliding toward the center of the record due to the centripetal force generated during playback.
Phono preamp
One of the most critical components for enjoying sound from a turntable is the phono preamp or phono stage. Purchasing a phono preamp is a crucial step for any vinyl lover looking to elevate their listening experience. Its role is to amplify the weak signal produced by the turntable's cartridge and convert it to a level that your audio amplifier can handle.
Check out the detailed Buying Guide for phono preamps here
With PreampSome: turntables have a built-in preamp, allowing them to connect to any type of amplifier or speaker.
Without Preamp: These turntables require an external phono preamp or an amplifier with a phono input.
Choice: If you don’t have an external preamp, a turntable with a built-in one can be more convenient. However, external preamps often provide better sound quality.
In general
Key points / Connectivity
- Analog RCA Output: The standard method for connecting to an amplifier or speakers.
- USB Connection: Allows for easy digitization of your records via a computer.
- Bluetooth: Some models support wireless connection to speakers or headphones.
- Choice: Select based on your needs for flexibility and ease of use.
Budget
- Entry-Level (€100 - €400): Suitable for beginners, offering basic features and decent sound quality.
- Mid-Range (€400 - €800): Provides better build and sound quality, with more features and upgrade options.
- High-End (€800 and above): Aimed at audiophiles and professionals, these turntables offer top-notch sound and build quality.
Additional factors
- Maintenance: Consider ease of maintenance and availability of spare parts.
- Accessories: You may need additional accessories like cleaning brushes, anti-static mats, and stands.
- Warranty and Support: Check the warranty and support provided by the manufacturer.
Important specifications
Looking at pictures of a turntable won’t tell you much about its performance compared to other models. Manufacturers use specialized specs to help you make comparisons, so let’s break down what each one means.
- Signal-to-noise ratio: This measures how much background noise you hear. A higher number is better, as you want much more music signal than noise. Look for something above 65dB.
- Playback Speeds: Most turntables offer 33-1/3 and 45 revolutions per minute (RPM). If you’re buying a turntable to play 78 RPM records, it can handle modern "microgrooves" but not older vintage recordings. Ensure you have a specialized cartridge suitable for the wider grooves of these increasingly rare records.
- Wow and flutter: This spec tells you how precisely the turntable’s platter rotates. Too much variation can cause an audible warbling effect. A lower number is better here, ideally under 0.25%.
In Conclusion
Choosing the right turntable requires careful consideration of your needs and preferences. Take the time to research and, if possible, test different models before making your decision. A good turntable can provide you with years of enjoyment and truly enhance the beauty of vinyl in your music experience.
Happy listening!
If you need assistance choosing a turntable and matching it with preamps, amplifiers, and speakers, one of our expert advisors can discuss your existing equipment and what you might need to add. All of our advisors are knowledgeable, friendly, and love music as much as you do. Contact us today. And don’t hesitate to call us if you encounter any issues during the setup process. Every purchase from Athens Pro Audio includes free technical support.
AthensProAudio Team ©









